Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have been shown to provide overall cardiovascular benefits in type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients at high risk, according to a presentation at the recent American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Chicago.
At the same time, according to researchers in Thailand, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) showed neutral effects. In addition, they pointed to reports indicating that heart failure (HF) was significantly reduced with SGLT2i treatment but might be increased with saxagliptin, a DPP4i.
.jpg)
Glycated hemoglobin. Source: iStock
Noting that benefits and risks are still debated, the study team explained that SGLT2i and DPP4i have different cardio-metabolic effects, which contribute to different outcomes in T2D patients with coronary artery disease.
Their small study randomized of 44 T2D patients with established CAD who had hemoglobin A1C 6.5-9.0% to receive dapagliflozin (n=21) or vildagliptin (n=23) for 6 months. Excluded were patients with recent acute coronary syndrome, or acute decompensated HF, or estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30 ml/min.
Defined as cardio-metabolic parameters were anthropometric, glycemic index, lipid profile, renal function, hemoglobin (Hb), tumor necrotic factor (TNF) and interleukin-10 (IL-10); results of those tests were collected at baseline and the end of treatment for participants, who were 52% male at a mean age of 63.
Of the patients in the study, 27% had HF diagnoses and mean LVEF was 57%, according to researchers. No differences in baseline characteristics were identified between the two groups, which had mean HbA1C, systolic blood pressure (SBP), Hb level, LDL-C, HDL-C and eGFR were 8.2%, 124±18 mmHg, 12±2 g/dL, 92±38 mg/dL, 46±14 mg/dL, and 72±20 ml/min, respectively.
Results indicated that, at 6 months, HbA1C was reduced 0.8% in both groups with no difference in changes of LDL-C and HDL-C. Researchers pointed out that patients receiving dapagliflozin had significant reduction of body weight (BW), BMI, and SBP, and had significant increase in Hb level.
Furthermore, the changes in BW, BMI, Hb, high-sensitive troponin T (hsTnT) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were significantly different between groups, as shown in table 1.
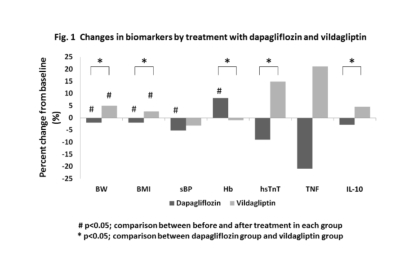
Table 1. Changes in biomarkers by treatment with dapagliflozin and vildagliptin
The study team wrote that one patient in dapagliflozin group developed non-fatal MI, but none of the participants experienced serious adverse effects from the treatment.
“Dapagliflozin and vildagliptin had different effects on hemodynamic and inflammatory markers,” study authors concluded. “These extra-glycemic effects may contribute to different CV outcomes.”
